It’s a Hike & Feast!! That’s right, we’re headed for a hike at the Guadalupe River State Park, about 30 minutes northwest of San Antonio off Highway 46, west of 281 North.
This was the very first state park I ever visited when I first started camping. At the time of this first visit, I was a poor, case manager. Bachelor’s degree in hand, first professional job, still making peanuts. My housemate and I were looking for ways to have some fun that didn’t cost a lot of money. We decided to try our hand at camping so we splurged on a tent and somehow, I don’t really remember how, we found this park, made a reservation and spent a lovely weekend sleeping on the hard ground, grilling meats, hanging out at the river, and just generally, enjoying nature.
This isn’t my favorite state park but it does hold a special place in my heart because it was where I discovered camping. I’d been to Rocky Mountain National Park with my college roommate and her family before this camping trip, but they had a pop-up trailer and all I had to do was sit back and let my friend’s dad be in charge. The trip to Guadalupe River State Park was my first time setting up my own campsite, starting a campfire, and all the other camping experiences that came with it, including the midnight trips to the bathroom. But it was all good because that little bit of camping led to backpacking which led to hiking and here we are today! It’s a full circle for me.
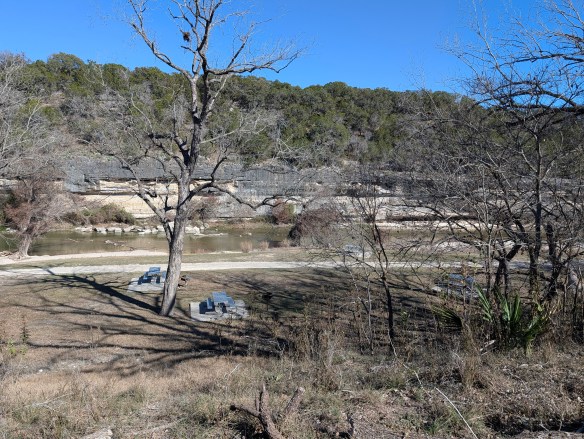

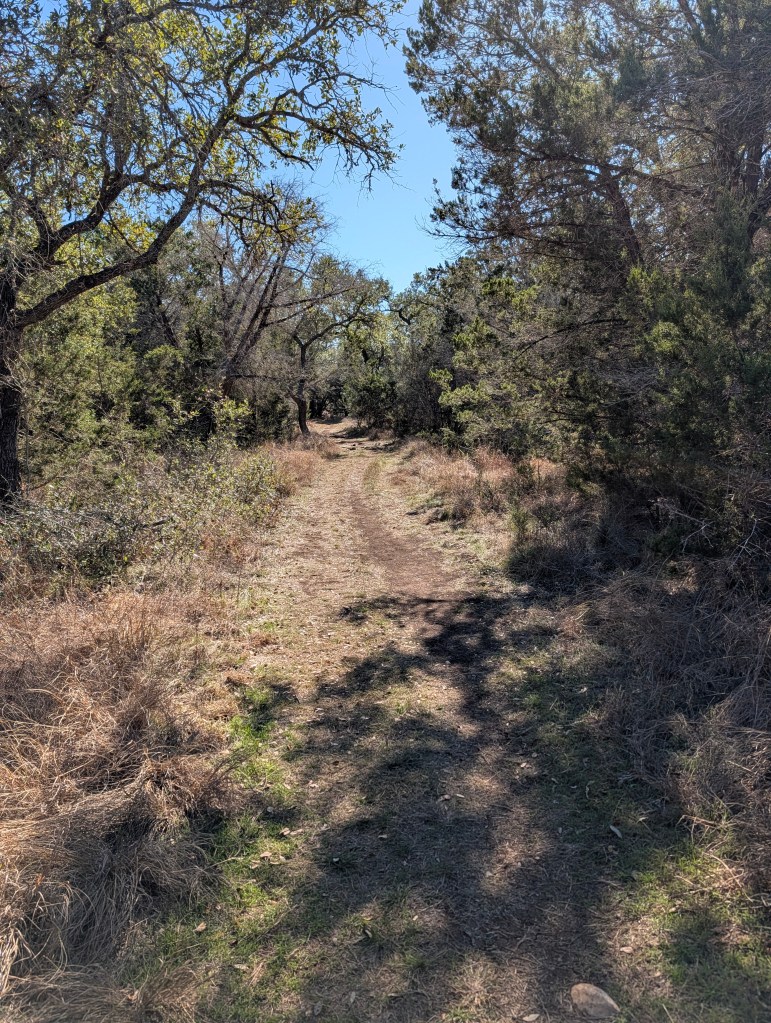
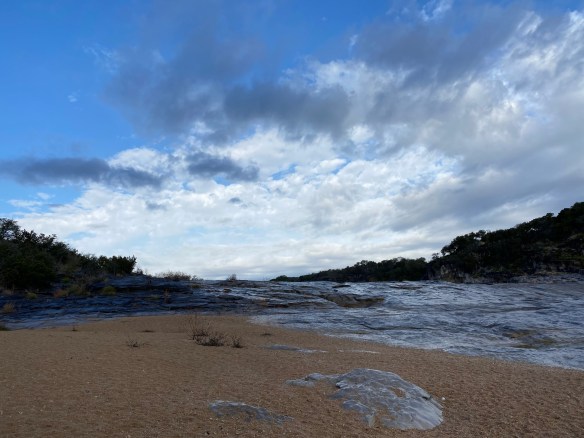
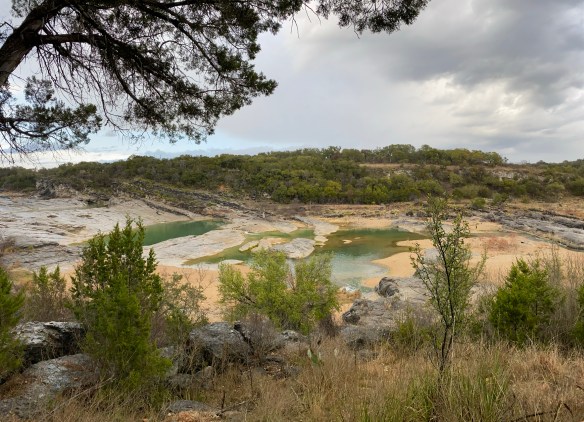
Guadalupe River State Park, as the name implies, sits smack dab on the Guadalupe River. The river here runs quiet and serene. The gentle flow makes it perfect for kids to get in and float down aways on a tube or raft, climb out, and do it all over again. The day use area is right on the river and you’d better believe it gets crowded in the summer. If you’re looking to camp here in the summer (as well as spring and fall if it’s warm enough), it’s going to be busy. It’s not the getaway you might be looking for if you’re looking for silence or quiet nature. But, if you’re looking for a place to hike some quiet, easy, and beautiful trails, you’ve come to the right place. Especially if you’re here in the fall and winter. Spring is also a magical time when the wildflowers are in bloom.
Guadalupe River State Park is part of the area we’ve discussed in some of our other blogs and in our podcasts. Like Pedernales River State Park and our first Hike & Feast at Crownridge Canyon Natural Area, Guadalupe River State Park is an area comprised of limestone canyons that used to be a seabed. Dramatic canyon walls and rocky outcrops were formed when this region was covered by a shallow sea millions of years ago. If you look closely at the limestone layers, sometimes you can find fossiliferous limestone, better defined as fossils of seashells and organisms fossilized right into the limestone. Bonus if you’re a birder! This park sits at the crossroads of Hill Country and riparian ecosystems, making it an important stopover for migratory birds. Fall hikers often don’t realize they’re walking through habitat used by golden-cheeked warblers, painted buntings, and migrating raptors. Susan and I hiked the Painted Bunting Trail, named after the beautiful painted bunting bird (which we did not see while we were hiking, damn it).
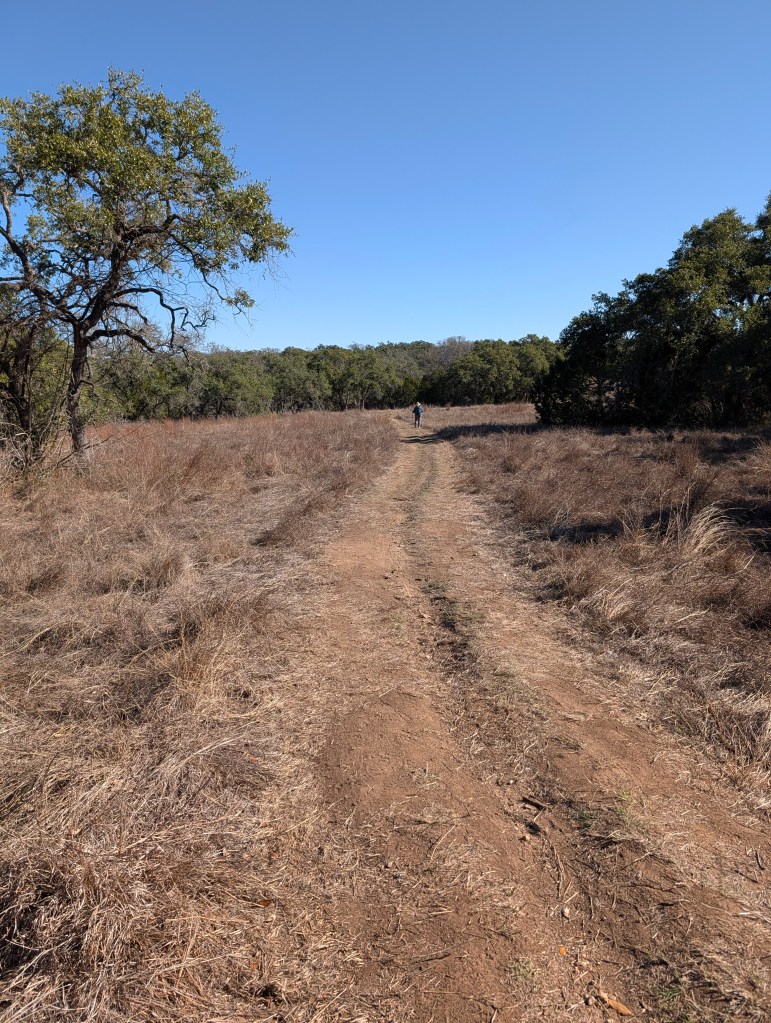
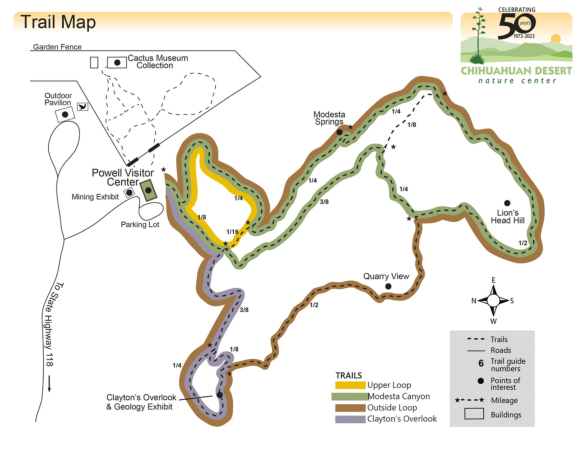
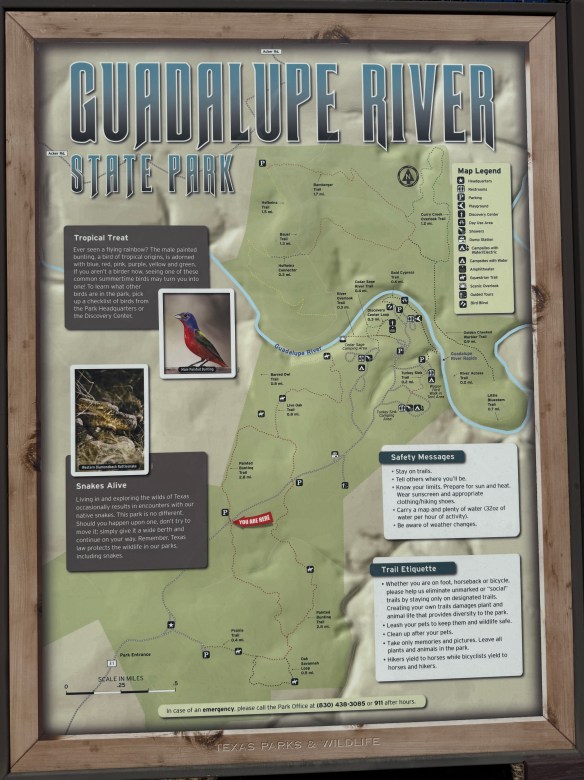
This park has plenty of trails ranging from easy to challenging. Trail lengths range from 0.3 miles all the way to 3.1 miles. There are also river crossings if you’re looking to roll up your pants and get your feet wet. Terrain is varied and there are some trails that are short but steep, so choose wisely.
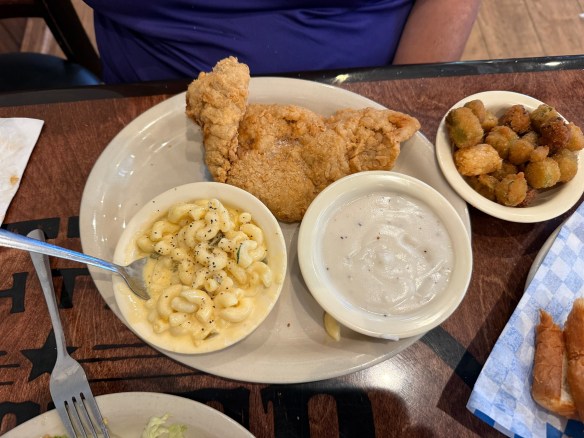
This is a great, little getaway right down the road from San Antonio. And there are plenty of places to feast after you finish up your hike. We made our way a few miles up the road to Spring Branch, Texas where we feasted on chicken fried steak at Antler Cafe. Delicious!

MILE MARKER: Guadalupe River State Park protects one of the cleanest stretches of the Guadalupe River. Unlike the more heavily trafficked downstream sections (like New Braunfels), this stretch of the river is spring-fed and less developed, which helps keep the water unusually clear and ecologically healthy. It’s a quiet reason why the park feels so calm compared to other Guadalupe access points.
HIKE IT!: Make sure you check out the park’s website hiking page for links to their trail map but notice that there’s a secret hike on there! That’s right, there’s a secret hike at the connected Honey Creek State Natural Area. Access to this special area is allowed only by tour which is a 2 mile, ranger led tour, that only happens once a week. Click on the link to get to the Honey Creek website and sign up for that special hike there.