There are signs that approximately 10,000-12,000 years ago, in the area we now recognize as the central Texas hill country, the Paleoindian people were utilizing the natural resources of the area to create tools for hunting megafauna such as bison and wooly mammoth. The grasslands of central Texas were the perfect environment for these animals. Add abundant water and flint, or as the Spaniards called it, pedernal, used to create those tools for hunting, and we can see why the area was such a draw for the indigenous people.
Fast forward to the 16th century, Spanish explorers and missionaries are making their foray inland towards central Texas. Lipan Apache are roaming the area and the Franciscans in charge of the missions in San Antonio are suggesting that a mission may need to be built in this part of Texas, as well. While that suggestion never comes to fruition, the influence of the Spaniards is cemented on the land. While in the area, the Spanish explorers begin to refer to the flowing water as the Pedernales River, due to the abundant amount of flint, or pedernal, in the riverbed.

After Texas became a state in 1845, small farming communities began to develop. and in the late 1800’s, the area in and around Pedernales Falls grew, but by the 1930’s, that same area began a decline. Lack of population growth, a depressed economy, and drought, probably helped to diminish and keep the local citizens to the bare minimum. The surrounding land was used for grazing until the original owner sold the land to Charles (C.A.) and Harriet Wheatley.
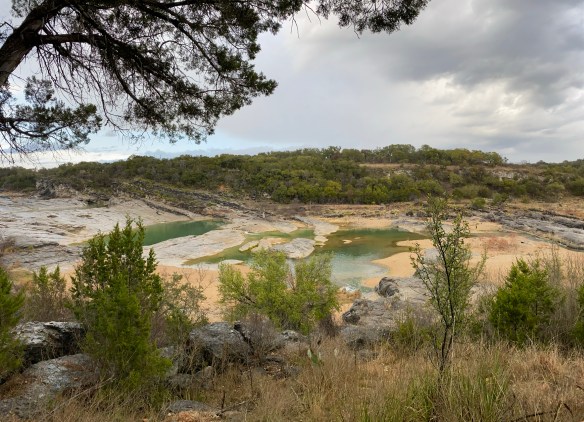

The Wheatley’s named their new ranch, the Circle Bar Ranch and began improvement projects. They built a road that connected their ranch to the nearest county road and began building their home. They brought in purebred Hereford cattle and eventually, steer and goats. Although the Wheatley’s enjoyed hunting, they strongly believed that natural resources should be preserved and protected for the enjoyment of future generations. The Wheatley’s were prolific conservationists. Charles Wheatley helped to organize the National Wildlife Management Institute and was one of the founders of the Texas Fish and Game Commission. He was a friend of Governor Neff, who was responsible for creating the Texas State Parks system. Harriet Wheatley was also a lover of nature who enjoyed hunting and was active in the San Antonio Conservation Society, the Bexar County Girl Scouts, and the Blue Bird Auxiliary. She and Charles were both known to be expert fly fishermen and she even published a book entitled, Lady Angler: Fishing Hunting, and Camping in the Wilderness Areas of America.

In 1969, Harriet Wheatley sold the ranch to the state of Texas with her wish that “that it be conserved, and all of the wildlife be taken care of, and that it be enjoyed from generation to generation.” The park officially opened in 1971 as Pedernales Falls State Park. The park’s terrain typifies the Edwards Plateau, with woodlands, cedar brakes, grasslands, and lush riparian zones lining the Pedernales River.
The Pedernales Falls State Park is located at 2585 Park Road 6026, Johnson City, TX 78636. The park is open daily open daily and the office is open 8 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. The park’s phone number is (512) 389-8900.
Accessibility: Call ahead for specific information regarding building accessibility. They do have an all-terrain wheelchair available for use in the park. Contact the park to reserve it for your visit.
MILE MARKER: Beneath the falls and limestone shelves, the riverbed preserves fossilized tracks of ancient creatures. If you look closely in certain areas, you can spot impressions of prehistoric marine life that lived here when the Hill Country was covered by a shallow sea more than 100 million years ago.
HIKE IT!: Ten trails, from easy to challenging, are available for hiking, biking, and horseback riding. Trails vary in length from half mile to ten miles mean there are trails for every type of hiker! For more detailed information about the types of trails, check out the hiking trails page on the Pedernales State Park website.